Assessing Risk Factors for the COVID Vaccine and Severity of COVID Illness

How does our immune system work? Where can it fail?
August 10, 2021
Supplement Instruction Sheet
September 3, 2021Many are concerned about the safety of the currently available vaccinations for the COVID-19 virus, particularly AstraZeneca. The information coming out of the latest statistics in the UK suggests people with inflammatory diseases such as autoimmune disease, for example, Rheumatoid arthritis, Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, Type 1 diabetes, Chrohn’s disease, or SLE may have a higher risk of complications.
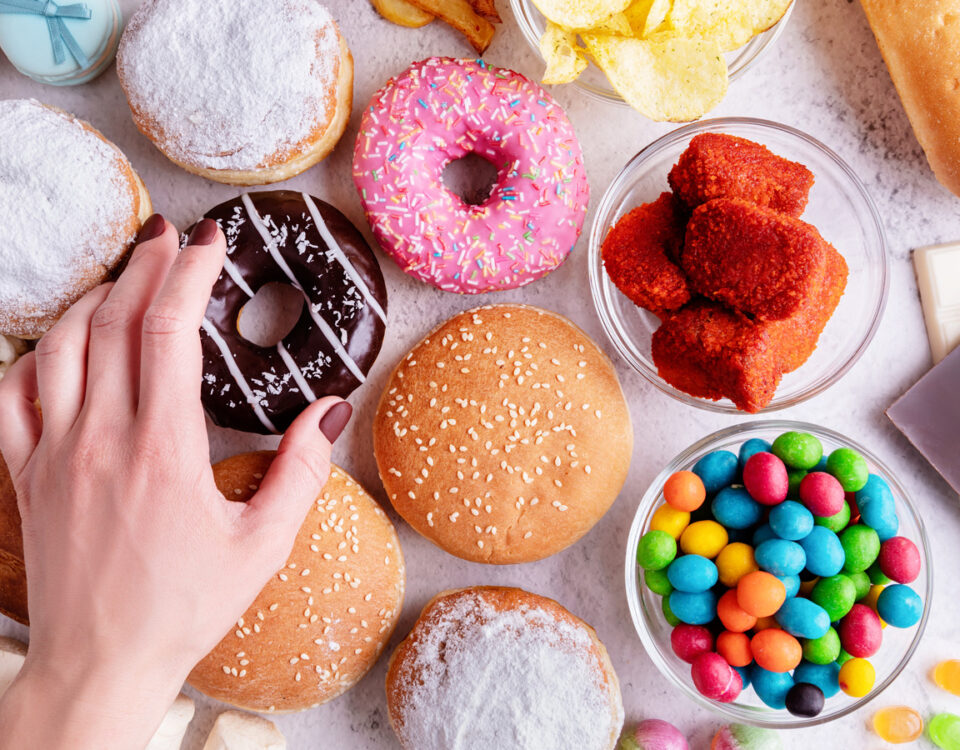
People with Type 2 diabetes, asthma, allergies, or arthritis, for example, may also have high inflammation that could be of concern for both the vaccination and the COVID-19 virus.
You can be between a rock and a hard place. Do you have the vaccine or risk serious complications of COVID if you don’t? We know that serious complications of COVID can occur with the inflammation storm that overwhelms the body in the 2nd phase of the disease. It is therefore most important to get pre-existing inflammation under control.
There are many lifestyle factors that we do have control over to reduce inflammation but firstly, let’s check out whether you have inflammation and if you are at risk.
Recommended testing for COVID vaccination safety
We look at markers for inflammation, blockages to major pathways for detoxification, and allergy markers.

1. Homocysteine
Homocysteine is part of a cycle called methylation that makes one of our body’s most important methyl donors to make brain chemicals, phosphatidylcholine for healthy cell membranes, facilitate sleep, liver detoxification, and more. In times of infection, we healthy cells and our methylation cycle to be working.
If this marker becomes too high, it may indicate that there is a block in the methylation cycle and high levels are associated with a higher risk of a cardiovascular accident such as stroke or heart attack, hardening of the arteries, and a higher risk of blood clots.
2. MTHFR gene
Approximately 20% of the population has a genetic variation of the MTHFR enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of methyl folate needed to kick start the methylation cycle mentioned above.
A simple test can check if you have one or two variants of this gene.
3. Full blood count and biochemistry
Includes markers for general health, kidney and liver function, and inflammation markers including HsCRP (high sensitive C reactive protein)
4. Cytokine Panel
To assess inflammatory cytokines (Cells). Too many inflammatory cytokines especially interleukin-6 (IL-6) facilitate out-of-control inflammation in the presence of the COVID virus.
High levels of inflammation may be associated with adverse effects of the COVID vaccine.
5. Lipids
These are the fats that makeup out cell membranes. A healthy balance of omega 6 to omega 3 fats promotes healthy cell membranes more able to withstand stress.
A high proportion of omega 6 fats or trans fats from takeaway foods promotes inflammation in the body and increased the risk of reaction to the vaccination and/or severe reaction from COVID.
6. Vitamin D (25 OH D)
Vitamin D is a key activator of the immune system in response to the invasion of a pathogen. Low levels have been associated with a more serious outcome from COVID and prolonged illness post any viral illness.
Blood levels need to be between 100-150 nmol/L. To get adequate vitamin D from the sun you need to have skin exposure for at least 30 minutes per day. In cold climates, the sun is not very strong and vitamin D levels have been shown to be low across that population.
If you live in a warmer climate but work indoors you will not get adequate vitamin D. Therefore, testing will give you an accurate assessment of your real-time vitamin D level.
7. Thyroid Panel
The thyroid hormones regulate metabolism in every cell in the body. A sluggish thyroid will impact the health of your immune response in the face of infection or a virus such as the Flu or COVID.
8. If you have Autoimmune disease
Test Antinuclear antibodies (ANA) to assess the degree of antibodies present and the current status of your autoimmune illness.
An extractable nuclear antigen (ENA) panel detects the presence of autoantibodies in the blood that react with proteins in the cell nucleus and are more specific to diagnose the type of autoimmune disease.
Autoantibodies are produced when a person’s immune system mistakenly targets and attacks the body’s own tissues. This attack can cause inflammation, tissue damage, and other signs and symptoms that are associated with an autoimmune disorder.
Certain autoimmune disorders are characteristically associated with the presence of one or more anti-ENA antibodies.
The ENA panel typically consists of a group of 4 or 6 autoantibody tests. The number of tests performed will depend on the laboratory and which autoimmune disease is suspected.
If you are concerned about whether you are at risk of complications post the COVID vaccine or your ability to deal with a COVID infection call on 02 66252925 or email me here.
Avail yourself of my FREE 20 minute chat either by phone or online
Please send me a message on the contact page and I will get back to you